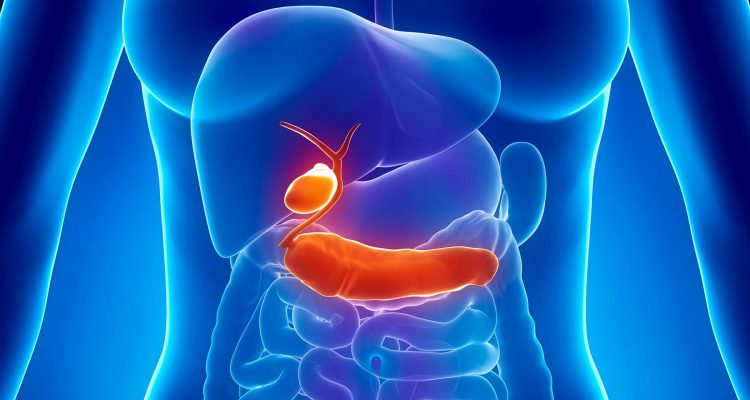
Violation of the contractions of the smooth muscles of the biliary tract and the sphincter of Oddi leads to uneven secretion of bile (primarily from the gallbladder). Not very dangerous in itself, the disease can lead to the development of gallstone disease.
Bile is a special fluid that is produced in the liver. Its main tasks are to improve the absorption of fats and to activate the movement of food through the intestines.
Before bile enters the intestines, it goes through a difficult path along the biliary tract. First, from the liver, it enters the hepatic ducts, from there into the common bile duct, which connects to the gallbladder through the cystic duct. The place where the common bile duct flows into the duodenum is called the Vater papilla. It has its own muscle (sphincter of Oddi), which regulates the flow of bile into the intestines.
Biliary dyskinesia is a disease in which, due to a violation of the contractions of the gallbladder and its ducts, as well as defects in the work of the sphincter of Oddi, problems arise with the excretion of bile.
According to statistics, women are more likely to suffer from biliary dyskinesia.
Causes
The development of the disease is facilitated by:
irrational nutrition (a lot of fatty, spicy, long breaks between meals);
diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis);
hormonal disorders;
menopause;
worms;
food allergy;
nervous experiences, stress.
What’s happening?
Doctors identify two main forms of dyskinesia. In the hyperkinetic form, the tone of the gallbladder is increased and its contractions occur too quickly and strongly. The sphincters (muscle “gates”) do not open up enough. This causes sharp pain in the right hypochondrium. The attacks of pain are usually short-lived and rarely last more than one hour. As a rule, they do not arise from scratch, but are provoked by negative emotions, worries, and nervous overloads. In women, exacerbations of the disease are associated with the menstrual cycle, since during menstruation, the tone of the gallbladder is usually increased. The hyperkinetic form of dyskinesia is more common at a young age.
On the contrary, older people are more likely to suffer from the hypokinetic form of dyskinesia. Its cause is insufficiently intense contraction of the gallbladder. It is also manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium. True, the pain is usually not strong, but prolonged, is dull, often bursting in nature. However, here, as in medicine in general, there is nothing absolute. All manifestations of the disease are very individual. It is not easy even for an experienced physician to make an accurate diagnosis based on patient complaints alone.
Biliary dyskinesia consists of a series of exacerbations and improvements. After some time, an inflammatory process (cholecystitis, cholangitis) or gallstones (cholelithiasis) may form in the gallbladder and ducts.
If in the morning you feel a bitter taste in your mouth, if you are constantly in a bad mood and fatigue, it is possible that the cause of all the troubles lies in the disruption of the biliary tract. And if, at the same time, about the time (over-excitement or having a snack with a spicy salad) you feel pain in the right hypochondrium: dull aching or, conversely, acute cramping, immediately go to an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Seventy out of a hundred chances you have dyskinesia.
Warning signs: constipation or diarrhea, poor sleep and appetite, decreased sex drive, and an irregular menstrual cycle (in women).
Treatment
It is important to establish the form of dyskinesia during the examination – the method of treatment will depend on this. A prerequisite for the treatment of dyskinesia is diet.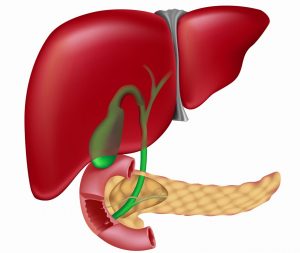
A diet with a hyperkinetic form is frequent fractional meals (4-5 times a day), restriction of foods that cause bladder contractions (fatty, meat products, vegetable oil, cakes and other products made from fatty dough, beer, carbonated drinks). Dishes should be mostly mashed and boiled, not too greasy or spicy. More fruits and berries in any form!
Of the drugs, antispasmodics are mainly used (no-shpa, etc.). Choleretic drugs (holosas, cholenzym, flamin) and medicinal herbal preparations (corn silk, rose hips, peppermint, etc.) will not be superfluous.
To this day, the ancient method of treatment is widely used – drinking mineral waters. With this form of the disease, waters with low and medium mineralization are recommended: Narzan, Navtusya, Slavyanovskaya, Smirnovskaya, Essentuki No. 4 and No. 20. Water should be drunk hot (40-25 degrees), ½ glass or 1 glass 3-4 times a day half an hour before meals.
If all of the above does not help, the doctor may prescribe a tyubage – washing the biliary tract.
A diet with a hypokinetic form must necessarily include foods with a choleretic effect: sour cream, butter and vegetable oil, cream, soft-boiled eggs, black bread, vegetables. They stimulate the motor activity of the biliary tract. For the same purpose, aloe extract, eleutherococcus, ginseng are used. Plant choleretic preparations help well. They usually include immortelle flowers, yarrow, mint leaves, coriander fruits, etc.
Choleretic agents https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholagogue are used – tsikvalon, 10% solution of xylitol or sorbitol, Karlovy Vary salt and herbs – parsley decoction, decoctions and infusions of medicinal dandelion, yarrow, marsh calamus, barberry.
Mineral waters are also used here, but only with a high degree of mineralization. For example, Batalinskaya, Arzni, Essentuki No. 17. They should be drunk cold ½-1 glass 3-4 times a day for 30-60 minutes. before meals (within 3-4 weeks).
In addition, a tubage with Karlovy Vary salt, magnesia sulfate or sorbitol is used.
Dyskinesia is also treated with physical therapy. In recent years, laser and acupuncture have been increasingly used.